Usted está aquí
Peruvian Journal of Neurosurgery
Clinical practice guide of congenital hydrocephalus
Minimally invasive treatment of Arteriovenous Malformations
ABSTRACT
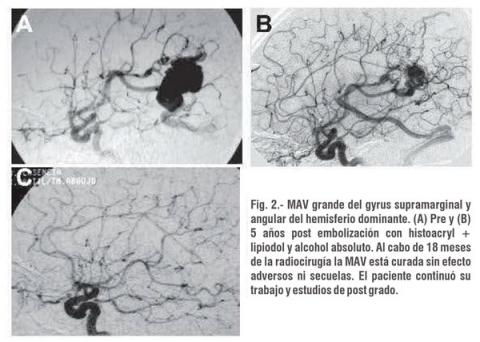
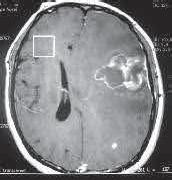
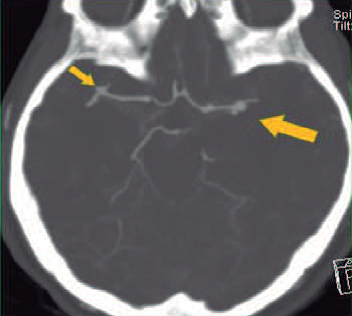
Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations (AVM) are the most common type of intracranial vascular malformation and are the second most common cause (after cerebral aneurysms) of intracranial hemorrhage. Anatomically, AVM is a set of embryologically immature and fragile vessels, located in brain tissue. Hemodynamically it constitutes a system of low pressure of turbulent flow that wears the involved dysplastic vessels, of there its tendency to break up and to bleed.
Cerebral Vasoespasm
ABSTRACT
Cerebral vasospasm can be defined as the focal or diffuse narrowing of the large and medium caliber capacitance arteries at the base of the brain that follows a hemorrhage in the subarachnoid space. Aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage is the major etiology for vasospasm, although it has also been seen after bleeding from an arteriovenous malformation, tumors, or traumatic brain injury. Its diagnosis is not always easy, and may have a temporary course; May be completely asymptomatic or be confused with another complication associated with subarachnoid hemorrhage. However, in more than 50 percent of cases, vasospasm is manifested by a delayed-onset neurological deficit, which can resolve and progress to permanent cerebral infarction.
Multicystic vertebral hydatidosis disease.
ABSTRACT
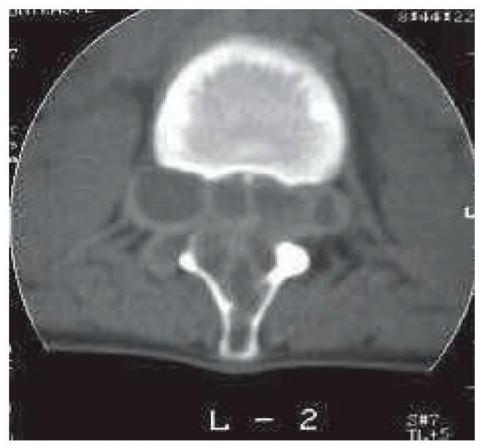
We report a rare case of dorsal-lumbar spine hydatidosis. The patient is a 15-year-old girl from Chincha, Ica who, due to persistent low back pain and progressive severe paraparesis of a year of evolution, is transferred to the Maria Auxiliadora Hospital. Radiographs, computed tomography, and MRI scans showed multiple vertebral cystic images at L1 and L2 levels with severe invasion of the vertebral canal, which were reported as probable aneurysmal bone cyst. The patient underwent previous percutaneous exploration and appropriate precautions for exploratory and decompressive surgery, evidencing multiple cystic vesicles compatible with spinal hydatidosis, which was later confirmed by pathological anatomy. The clinical recovery was gradual and without cystic recurrence
Showing total recovery with last control at 4 years of the intervention.
Key words: Spinal hydatidosis, hydatid cyst, spine surgery
Anterior Cervical microdisectomy without fusion. Preliminar experience in a center of the North of India
ABSTRACT
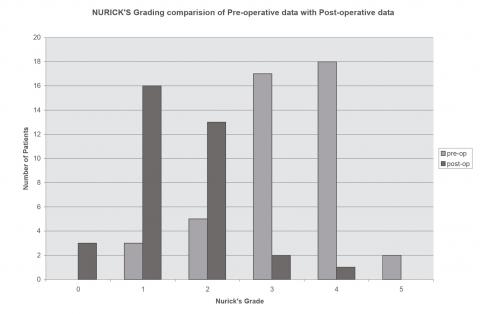
Patients and methods: From January 2004 to March 2007, patients with radiological evidence of one or two levels of cervical disc disease were included in the study and were followed for a minimum of 6 months and a maximum of 46 months. All patients underwent only previous cervical microdisectomy, by a single surgeon, using a Leica microscope. Patients were assessed for improvement of symptoms and clinical signs, work status using Nurick's graduation and Odom criteria.
Results: Of the 33 patients operated during the study period; 28 were males and their age varied from 28 to 65 years with an average of 45.72 years. The C5-6 herniated disc was the most commonly affected level. Five patients had two levels of disc herniation and were operated on two levels in the same surgery. The most common presentation was radiculomyelopathy followed by pain and myelopathy. Root pain was the earliest symptom that disappeared after surgery followed by myeloptic symptoms.
Conclusion: This technique is a suitable surgical treatment for the majority of cases of prolapsed cervical disc; Does not require fusion and avoids specific problems and complications associated with instrumentation and fusion. We, even continue the follow-up study of these patients, but to date no considerable late problem has become evident. We think that the best answer to this question can only be obtained with a prospective multicentric, double-blind, randomized study.
A rare case of complete anteroposition of C7 over T1
ABSTRACT
Cervical injury is common in the hills north of India. Rare types of clinical syndromes are seen due to falls from overweight height in the head. Anterior subluxation of the neck occurs most commonly in the mobile segment of the cervical region 4 (50% in the C5 / 6 joint), high or very low subluxations are rarely reported. We report an unusual case of complete cervical lesion with overlap and antero-position of the C7-T1 segment. We will discuss the various possibilities of complete low cervical subluxation with the review of the existing literature.
Brain abscess: Clinical and therapeutic study in a county hospital in Peru
ABSTRACT
The onset symptoms are: headache in 50%, seizures 17%. The main symptom: convulsions in 66%, hemiparesis and alterations of the sensorium. The clinical picture was characterized by headache (83%), convulsions (66%), hemiparesis (66%), fever (66%), aphasia (50%), papilloedema and vomiting (50%) Meningeal and prefrontal signs (33%). Clinical syndromes: headache (83%), focal neurological (83%), focal (67%), febrile (67%), HEC (50%), meningeal (33% %).
CT scan and cerebral MRI revealed 6 cases of cerebral abscess, of right hemispheric location in 5 cases, 3 single and 3 multiple cases; 2 in the frontal lobe, 1 frontalparietal, 1 frontotemporal and 1 parietal. Two cases in cerebritis and 4 encapsulated phase, with surrounding edema and mass effect. The treatment was done with cefotaxime 1 gr c / 6 hs. VEV / 20 days, or ceftriazone 2 g c / 12 h VEV / 20 days, together metronidazole 500 mg c / 6hs. EV / 20 days. In 1 case the treatment was prolonged up to 60 days with oral metronidazole. The sequelae were: hemiparesis, prefrontal alterations, convulsions, metronidazole peripheral polyneuropathy. The clinical and tomographic evolution was favorable in 4 cases, 2 patients died.
Odontoid fracture type II
ABSTRACT
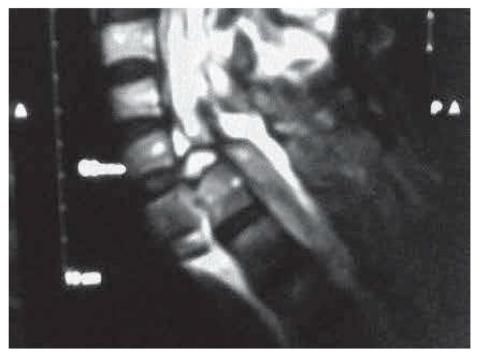
Odontoid type II fractures are relatively frequent and its therapeutic approach continues to be subject to considerable debate by the different column groups, both national and international. It is a young woman who suffered a traumatic brain injury in a traffic accident although there was no neurological compromise, persistent neck pain led to the diagnosis of a type II odontoid fracture. Faced with refractoriness to conservative treatment the patient was taken to surgery, in which an anterior fixation of the odontoid process was performed.
Odontoid fractures type II can be treated with a surgical or medical approach, each with advantages and disadvantages and in any case none free of morbidity. Surgical treatment is indicated by the failure of the conservative approach.
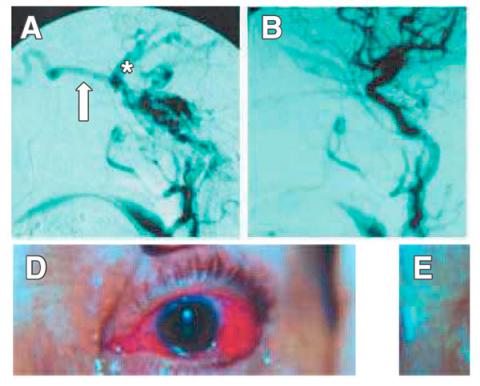
Endovascular Embolization of Cavernous carotid fistulas. Personal experience 1994- 2004
ABSTRACT
Patients and methods: Clinical and radiological data from 21 CCF treated between October 1994 and July 2004 were retrospectively analyzed.
Results.- Of 21 CCF 13 were direct and 8 indirect. The most frequent symptoms were red eye, murmur, exophthalmos and diplopia. Of the 21 CCF treated by endovascular techniques in the present study, 85.71% (18/21) were cured. An additional CCF was obliterated almost completely, constituting 4.76% (1/21). The attempt of embolization by both vascular routes was failed in 2 cases (2/21), 9.52%. Symptomatic complications occurred in a total of 9.52% of the cases (2/21), having a permanent neurological character in 4.76% (1/21) and transient in 4.76% (1/21%). The cured patients in our series improved their symptoms of orbital congestion in a few weeks while the paresis of oculomotors improved slowly or did not change from the preoperative period during the observation period.
Conclusion.- The endovascular embolization of the present series of CCF proved a very effective and safe treatment, managing to cure or improve in a significant and permanent way a vast majority of patients with results comparable to those reported in the international reference centers.
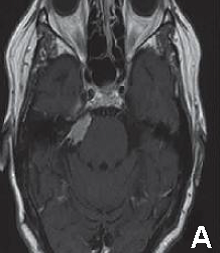
Endoscopic endonasal approach of Pituitary macroadenoma. First experience in Peru 2008
ABSTRACT
Management of multiple intracranial aneurysms
ABSTRACT
Multiple intracranial aneurysms (AIM) are relatively common, occurring in approximately 23% of all patients with aneurysms. The risk factors include female gender, hypertension, smoking and family history possibly intracranial aneurysms or cerebrovascular disease. The ruptured aneurysm location can be determined with a high accuracy rate with digital angiography when used in conjunction with computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance (MR). The average breakdown of untreated multiple aneurysms is between 1 and 2.2%. The critical size associated with significant risk of bleeding was 7 mm. Multiple aneurysms occur most often along the internal carotid artery (ICA) and the bifurcation of the middle cerebral artery (MCA). After bleeding is of any of the aneurysms, you must diagnose what was it bled, and which should be the first to be clipped, this is important especially when all aneurysms can not be clipped with a single approach. Most multiple intracranial aneurysms of the anterior circulation can be clipped by fronto-temporo-sphenoid approach; inclusive aneurysms on the contralateral side.Also, the development of new endovascular techniques (use of hidrocoils, bioactive coils, onyx, remodeling techniques with balloon or stent aneurysm single or double), permit more satisfactory treatments, including combining both techniques.
Conclusion: Multimodal approaches combining microsurgical and endovascular treatment, have been used successfully in cases of multiple cerebral aneurysms.
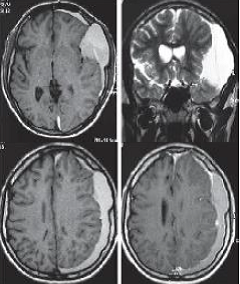
Chronic Subdural Hematoma in young patient: Complicated congenital Arachnoid Cyst
ABSTRACT
Chronic subdural hematoma (CSDH) is a common pathology in daily neurosurgical practice that usually develops in older people due to brain atrophy related to age, being rare in young people. We report the case of a patient of 16 years with a HSDC formed a left temporal congenital arachnoid cyst, which
simulated a meningioma plane, which was operated by craniotomy and resection of membranes, and its postoperative course was favorable Young people may also have HSDC if they have similar conditions that favor developmentof chronic subdural hematoma in the elderly, such as a congenital arachnoid cyst, which is a major risk factor for chronic hematoma in young and should be considered in the differential diagnosis of these lesions. Surgical treatment may be performed by trephination and irrigation or by craniotomy.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery in Neurinomas and Meningiomas of Skull Base
ABSTRACT
We report our experience with LINAC stereotactic radiosurgery for tumors of the skull base: 32 patients (21 meningiomas and 11 acoustic neurinomas) tracked over 20 months between November 2004 and July 2010. 17 received before radiosurgery, surgical treatment with partial tumor resection. With a median of 32 months after radiosurgery, tumor control is evident in 97% of cases, including 10 cases had tumor regression and tumor necrosis 12, making 22 cases with frank tumor regression. 9 patients remain under observation with no change in tumor size but incipient necrosis. A patient with acoustic neuroma showed tumor growth at 36 months of observation for which he received a second treatment with radiosurgery. Among the functional effects of radiosurgery., 9 of the 10 patients with trigeminal neuralgia were recovered, 2 of 3 cases with oculomotor nerve paresis and 1 patient with ptosis recovered normal ocular motility. A patient with neurofibromatosis 2 deaf evolved despite its tumor regression. Benign tumors of the skull base have their personalized treatment option, either as primary therapy after subtotal resection or recurrence, radiosurgery is the best choice because it provides high rates of regression with control or low risk of complications.
Percutaneous microcompression of the Gasser ganglion for trigeminal neuralgia. Clinic Maison de Santé 2005 – 2009
ABSTRACT
Objective: Demonstrate the effectiveness of the percutaneous microcompression of the Gasserian ganglion with the balloon of Fogarty in the surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia.
Patients and methods: There was realized a descriptive retrospective and prospective study of 24 patients with trigeminal neuralgia treated surgically by the technique of percutaneous microcompression of the Gasserian ganglion with the balloon of Fogarty in the Clinics Maison de Santé between January 2005 until December 2009. The medical records and operative reports were review and the data were grouped according to study variables.
Results: The 66.7% of patients were female. The mean ages for the patients were 63.1 +/- 11.9 years and the average time of the disease was 8.1 +/- 4.8 years. The right side of the face was the most affected in 70.8%, and the trigeminal branches most affected were the combination of the second and third at 50%. The mean operating time was less than 30 minutes. In 91.7% of patients had no facial pain after surgery and no recurrence at one year by 83.3%.
Conclusions: The percutaneous microcompression of the Gasserian ganglion with the balloon of Fogarty is a highly effective technique in the surgical treatment in patients with trigeminal neuralgia.
Trigeminal Neuralgia by cerebellopontine angle epidermoid cyst
ABSTRACT
Trigeminal neuralgia is classically described as one of the most severe facial pain syndromes. Usually it is defined as a paroxysmal, lancinating, electric-type pain, recurrent and usually unilateral, in the distribution of one or more divisions of the trigeminal nerve. Typical trigeminal pain is characterized by intermittent, generally with periods of exacerbation and remission. The annual incidence of this pathology varies between 4 and 13 per 100, 000 individuals. The male:female ratio is 1:1.5. Although cause of trigeminal neuralgia is idiopatic, exist cases associated to compression of the trigeminal nerve by a vascular structure or tumors. Epidermoid cysts are tumors of embryological origin that are located in cerebellopontine angle in third place after schwannomas and meningiomas. Three cases of trigeminal neuralgia in relation to epidermoid cysts of the cerebellopontine angle compressing the trigeminal
nerve are presented. Clinical presentation, diagnostic studies, surgical treatment and postoperative results are discussed.
Key words: Trigeminal neuralgia, trigeminal nerve, epidermoid cyst, neuropathic pain, cerebellopontineangle.