Usted está aquí
Peruvian Journal of Neurosurgery
Clinical practice guide of Brain tumours
ABSTRACT
Currently four types of treatment are used: Surgery, Radiotherapy (RT), Chemotherapy (QT) and Immunotherapy (IT). Surgery is the most common treatment for intracranial tumors. RT is the use of X-rays or gamma and its purpose is to eliminate tumor cells from the outside and reduce their size (external beam RT); RT can also be used by placing radioactive materials into the tumor, through thin plastic tubes, radioisotopes, in order to remove the tumor cells from the inside (internal RT). QT uses drugs to kill tumor cells. It can be administered orally, parenterally or intrathecally; QT is considered a systemic treatment.
Alfonso Asenjo Gomez
ABSTRACT
A hundred years after his birth his memory is perpetuated in the Institute he founded and which today bears his name and in the hearts of those who had the privilege of being his disciples. From the beginning, Asenjo imposed a system of work different from that taken in other hospitals. Full dedication to the specialty, full time in the service, that is from 8 am to 6 pm, All clearly stipulated activity, schedule of clinical meetings, surgical ward programming, neuropathology meetings, general visit on Fridays, clinical meeting on Saturdays , Etc., all recorded in a small manual called "Routines", which also stipulated what we now call protocols for the study of each particular neurological pathology. At one time the Institute became "one of the most active in the world" in the words of E.A.Walker.
Clinical and radiological results of transpedicular fixation in symptomatic spondylolisthesis in adults
ABSTRACT
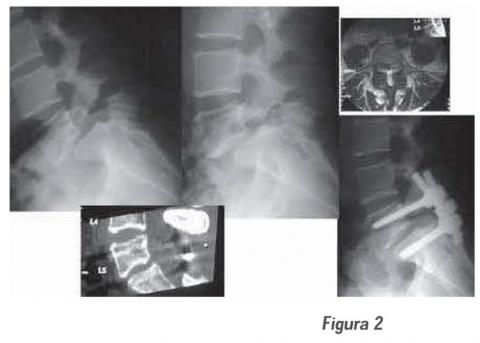
Retrospective, descriptive and analytical study of 34 patients, women 18, men 16; average age 50.8 years, with diagnosis of degenerative and isthmic spondylolisthesis (with degenerative component), Treated surgically with transpedicular fixation (FT) + arthrodesis Posterolateral (APL), in the Department of Neurosurgery of the Guillermo Almenara National Hospital between January 1966 and December 2004. The preoperative symptomatology was lumbar pain, neurogenic claudication and root pain. The predominant lesion level was L4-L5 and L5-S1. The degree of listesis Was: I: 6, II: 26 and III: 2. The reduction of the listesis was: total 18, partial 14 and non-reduction 2. The postoperative was with total or partial remission of low back pain in 31 (91%), total remission of neurogenic claudication and root pain in 30 (100%). The Oswestry Scale (functional disability) average: preoperative 64% and postoperative 24%, showed a significant difference (p <0.05). The persistence of residual low back pain mild in 25 (73%) was not associated with the degree of reduction of the listesis (p> 0.05). This results Demonstrate that FTP associated with APL optimizes the results of symptomatic spondylolisthesis surgery of adults with a progressive neurological condition that does not improve with conservative treatment.
Transoral decompression and posterior fixation in atlanto – axial instability
ABSTRACT
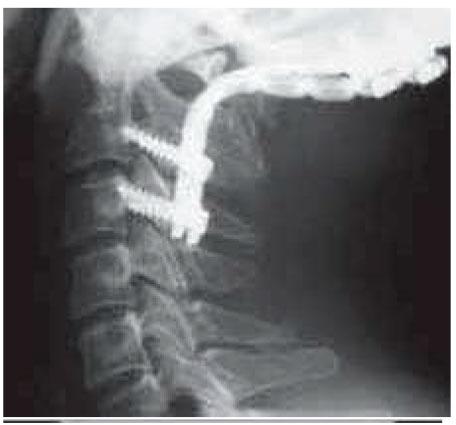
Objective: We review a description of the surgeries performed at the occipito- Atlanto-Axial segment in order to present the experience of the lesions diagnosed and managed at this level that required anterior decompression. An odontoidectomía was performed due to the irreducible nature of the lesion and/or because the mechanism of compression in the front, which were not susceptible to posterior approach.
Patients and methods: We report six cases in which, was used an trans oral technique to deal with the upper cervical spine segment. The cases were: four cases of rheumatoid arthritis and 2 cases of basilar impression. We described the clinical picture and the surgical technique used. Then we described the techniques used for posterior stabilization in each case.
Results: The first patient operated corresponded to a basilar impression and had dehiscence of the uvula and 1 patient (case 4) died a month after surgery due to nosocomial pneumonia and one pending fixation. The remaining patients were showed clinical improvement of symptoms and good consolidation later.
Conclusions: The trans-oral decompression surgery should be indicated in irreducible injuries and lesions where the compression is above, is recommended in other aetiologies abnormalities of bone, soft tissue or vascular. Transoral decompression - Atlanto axial instability - posterior fixation.
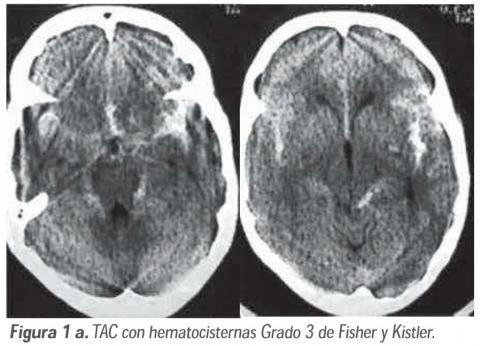
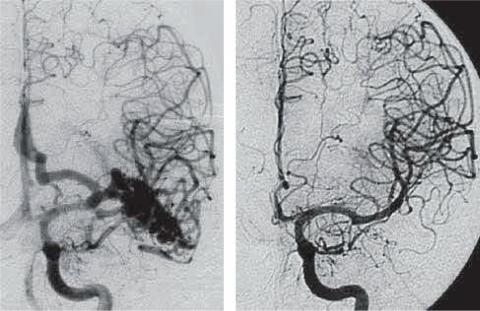
Cerebral vasospasm in subarachnoid hemorrhage due to ruptured cerebral aneurysm: Pathophysiology and treatment
ABSTRACT
Despite the large amount of experimental and clinical research that has been carried out in order to find a way to prevent and treat cerebral vasospasm secondary to subarachnoid hemorrhage caused by a ruptured brain aneurysm, this is a devastating complication. The first part of this review outlines the most important and recent experimental studies that have contributed to the advancement in understanding the mechanisms leading to cerebral vasospasm. The second part deals with therapeutic trials, based on this pathophysiological knowledge. The prevention and treatment of vasospasm or "narrowing" of the great arteries of the base of the brain, and the prevention and treatment of the consequence of this arterial "narrowing", the delayed ischemic deficit, reviewing the most accepted medical treatments.
Key words: Subarachnoid haemorrhage; Cerebral vasospasm; Impaired ischemic deficit.
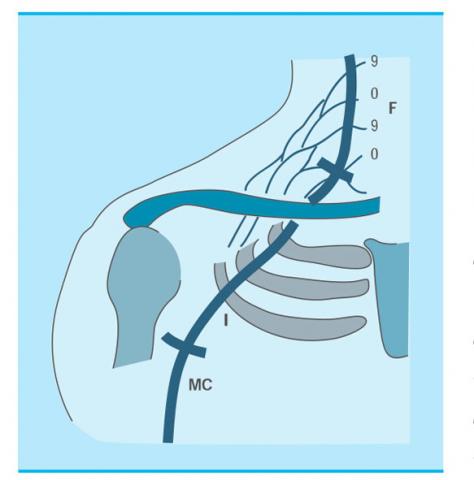
Neurotization in braquial plexus injuries of adult patients: Technique and results
ABSTRACT
Objective: To analyze the recently reported technical innovations in the reconstruction surgery of brachial plexus injuries.
Patients and methods: A total of 89 articles were analyzed, of which 50 were selected to perform this work. Priority was given to those studies describing technical innovations or large series that include the results of such techniques. The period analyzed was from January 1993 to June 2006.
Results: Numerous neurometric techniques of the plexus terminal branches have been developed in the last decade, including the use of spinal accessory, phrenic, ulnar, intercostal, C3-C4 cervical roots, contralateral C7 root and hypoglossal nerve.
Conclusions: Neurotization of the suprascapular and musculocutaneous nerves with the accessory spinal, phrenic and intercostal nerves show good results. In case of incomplete injury, the neuromuscularisation technique of the musculocutaneous with the ulnar (Oberlin) should also be considered. Unlike what happens at the facial level, the hypoglossal is not useful for neurotizing the brachial plexus.
Key words: Brachial plexus lesion, phrenic nerve, intercostal nerves, neuropathy.
The habit of smoking and the spine
ABSTRACT
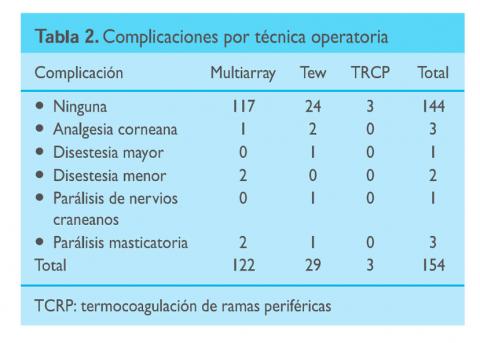
Cuadripolar electrode computarized method in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
ABSTRACT
A recent extensive review of the results of conventional percutaneous thermo-coagulation indicated that it is the most effective percutaneous technique with the highest residual morbidity.
The present communication is the summary, results and recommendations of our original method, designed to minimize unnecessary morbidity of the procedure. It is based on 31 years of experience in 370 procedures, most of the last 167 performed with our method and technique.
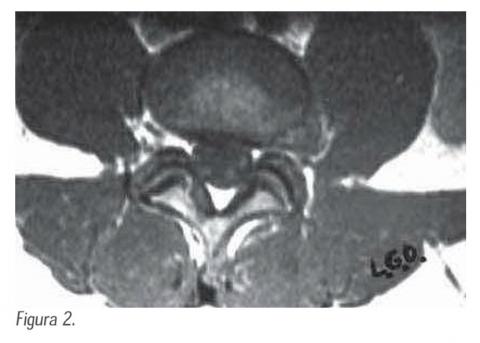
Diagnosis and treatment of extraforaminal lumbar disc herniation
ABSTRACT
Objective: Retrospective study to determine the number of patient with hernial disc in a traverse anatomical cut of the spine, the localization of them and also It Making emphasis in the cases with extraforaminal lumbar disc or call far lateral disc herniation.
Patient and methods: 159 patients were identified during the period of the years 2002 at the 2005 that were operated of lumbar discectomy, we presented hernial disc, The localizations committed was L4-L5 and L5-S1 and a small group in L3. We review the record of the patients with hernial disc extra foraminal and all patients were diagnosed them for study of magnetic resonance image, to determine the clinical square. The surgical technique is described.
Results: Five patients presented hernial disc extra foraminal, one patient presented foraminal and extra foraminal disc herniation, four of them were male and two women. In all them the pain symptom prevailed to level of the knee and anterolateral of the thigh in its half third under the knee, in two of the patients, the rehabilitation treatment was required to present deficit motor for the extension of the leg.
Conclusions: 3,77% of the patients presented extra foraminal disc and the presence of them should be suspected when the clinical square is of the lumbar high levels and the images of Resonance or CT scan are not conclusive for posterolateral disc herniation, in these cases it can be defined with CT scan with discography.
Coblation: New alternative in the treatment of sciatica for disc herniation
ABSTRACT
In the treatment of sciatica due to lumbar disc herniation, multiple surgical techniques have been used, from the traditional open surgeries to remove part of the intervertebral disc for decompress and reduce the pressure of this on the root, until its evolution into smaller incisions that allow decompression using the surgical microscope or through the use of endoscopy to access the disc. In some patients, however, even less invasive methods may be used for decompression. These alternatives are varied and are grouped within the percutaneous procedures being used basically in those patients whose pain is originated by a contained hernia.
Traumatic epilepsy in children
ABSTRACT
The encephalocranial trauma (ECT) in children is a health problem of great social repercussion with a high incidence worldwide, whose main causes are falls from height and traffic accidents. The relationship between ECT and traumatic epilepsy has been known since the time of Hippocrates (460-357 BC), who in his treatise 'Cranial Trauma' observed that a wound in the left temporal region of the skull produced convulsive seizures in the right hemisphere and vice versa. With industrialization and particularly with the advent of motorized vehicles, residences with different levels of height and unprotected and violent sports practices, the number of cranioencephalic injuries and, consequently, traumatic epilepsy has increased alarmingly.
Clinical practice guide of Myelomeningocele
ABSTRACT
Myelomeningocele, an open defect of the neural tube, is the most common congenital anomaly of the central nervous system (CNS) and the main cause that determines a number of growth and developmental disabilities in the affected child. It occurs due to a failure of the closure of neurulation in the caudal neural plate during the fourth week of gestation (22 to 26 days of gestation). It is characterized by dorsal protrusion of the meninges through a bony defect at the level of the spinal midline, without a dermal covering, forming a sac containing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and neural tissue Dysplastic, and which is usually associated with paralysis of the spinal nerves.